Pipeline
EBI provides a treatment for postoperative complications following major surgery, such as cardiac surgery. The initial focus is on complications associated with cardiac surgery, including Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting (CABG) and valve replacement procedures. Additionally, EBI has identified various other product applications for its first-in-class peptide drugs in various stages of development.

POSTOPERATIVE COMPLICATIONS
Postoperative clinical complications are truly a silent pandemic. With 312 million major surgeries performed each year globally, of which 40-50 million in the USA and 20 million in Europe, the prevalence of postoperative complications (27%) is immense and represents an enormous unmet medical need. There are over 700.000 CABG surgeries being performed each year in Europe and the US. For these procedures the incidence of complications range even higher, between 30 and 40%.
Postoperative complications have a striking socioeconomic and public health outcome and are in desperate need of an effective treatment option. EA-230 provides both a medical benefit to the patient in reducing treatment of postoperative complications as well as a substantial economic benefit reducing additional healthcare expenses.
Development Pipeline
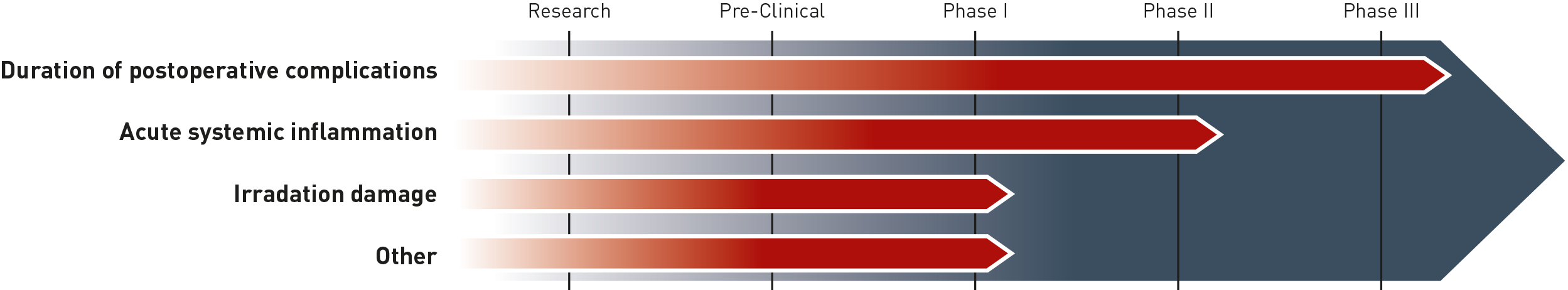
other applications
ACUTE SYSTEMIC INFLAMMATION
A second application of EBI’s product focuses on treating acute systemic inflammation. The prevalence of systemic inflammation is very high, affecting one-third of all in-hospital patients, and over 50% of all ICU patients. Trauma patients in haemorrhagic shock as well as patients receiving high doses of irradiation are at particularly high risk of systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS) and sepsis. Sepsis may occur in approximately 25% of ICU patients, and bacteraemic sepsis in 10%. In such patients, sepsis evolves to severe sepsis in over 50% of cases, whereas evolution to severe sepsis in non-ICU patients is about 25%.
Irradiation damage
EBI’s product may also be applied in the treatment of general irradiation damage. Of the people diagnosed with cancer circa 50% require irradiation therapy, 60% of whom are treated with curative intent. However, irradiation therapy is also related to severe risks. The response to radiotherapy is associated with several complications including debilitating damage to mucosal tissue. Currently, there are no safe and effective pharmacological agents to reduce irradiation toxicity that can be used in all patient groups.
Future indications
After successful development of EBI’s lead product for postoperative complications, systemic inflammation and irradiation damage, EBI’s pipeline provides a path forward for the development of new and promising critical care therapies for multiple organ damage related to hemodynamic instability and fluid overload, as well as, potential treatment of selected orphan diseases such as Clarkson’s disease (CLS) and Macrophage Activation Syndrome (MAS).

